Introduction
NSX Advanced Load Balancer (NSX ALB) is a multi-cloud software-defined load balancer that provides scalable application delivery across any infrastructure. NSX ALB is 100% software-defined and some of the key features include:
- Multi-cloud: Consistent experience across deployment of on-premises and cloud environments through central management and orchestration.
- Intelligence: Built-in analytics drive actionable insights that make autoscaling seamless, automation intelligent, and decision making easy.
- Automation: 100% REST APIs enable self-service provisioning and integration into the CI/CD pipeline for application delivery.
NSX ALB Use Cases
The key features driving the customers towards NSX ALB adoption are:
- Load Balancer refresh.
- Multi-Cloud initiatives (sysin).
- Security including WAF, DDoS attack mitigation, achieve compliance (GDPR, PCI, HIPAA).
- Container ingress (integrates via REST APIs with K8s ecosystems like GKE, OpenShift, EKS, AKS, TKG).
Architecture and Components of NSX ALB
The diagram below shows the high-level architecture of NSX ALB.
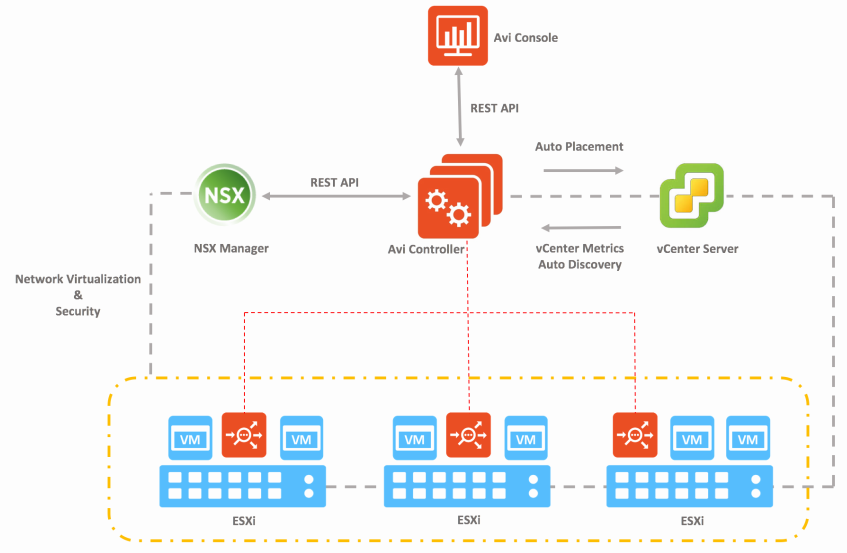
Figure 1 - NSX ALB Architecture
As shown in Fig 1, the NSX ALB controller acts as an entry point for UI/API operations for services and management. The controller interacts with the vCenter Server and NSX-T in an SDDC via API for auto-discovery of SDDC objects like ESXi Hosts, Network port groups, etc. The Service Engines are placed on the ESXi host and perform the L4/L7 load balancing for the applications deployed in the SDDC.
NSX ALB consists of two main components:
- NSX ALB Controller: NSX ALB Controller is the central repository for the configuration and policies and can be deployed in both on-prem environments or in the cloud. NSX ALB Controller is deployed in VM form factor and can be managed using its web interface, CLI, or REST API.
- Service Engines (SE): The Service Engines (SEs) are lightweight data plane engines that handle all data plane operations by receiving and executing instructions from the controller.
The controller handles the following tasks:
- All platform related configuration is done on controllers.
- Manage and store all policies related to services and management.
- Responsible for deploying Service Engines (sysin).
- Manage the placement of virtual services on SEs to load balance new applications or scale-up capacity of current applications.
- Facilitates UI console to perform the configuration and management.
- Host API services and the management plane cluster daemons.
The responsibilities of Service Engines are:
- Perform load balancing and all client and server-facing network interactions.
- Collect real-time application telemetry from application traffic flows.
- Execute data plane application delivery controls operations, such as health monitoring and test the performance of the back-end servers.
- Protect against security threats (DoS, suspicious client IPs).
Why you should choose NSX ALB
Traditional hardware load balancers have the following limitations:
- No Auto Scaling when load balancer runs out of capacity for the virtual service placement
- No Self-healing in a failure scenario
- Manual Virtual Service placement
- Complex upgrade procedure
- Compatibility with various platforms/cloud infrastructure.
NSX ALB is a 100% software-defined solution designed to address the above challenges.
NSX ALB Use Cases in VMware Cloud on AWS
- Load balancing of application inside an SDDC.
- Global load balancing across 2 or more SDDCs in VMware Cloud on AWS or between on-prem environment and an SDDC running in VMware Cloud.
- Integrates with Tanzu Kubernetes Cluster (TKG) to provide load balancing functionality for the Kubernetes workloads.
- Utilize NSX ALB in a hybrid model to provide load balancing of applications stretched between on-prem datacenter and SDDC in VMC.
下载体验
VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer (NSX ALB) 21.1.3
- 百度网盘链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/19WE6pwN3a8OphNxuL4h4lg 提取码:p1jc
下载仅供下载体验和测试学习,不得商用和正当使用。
下载体验

